10 Danger Signs of Diabetes Foot Complications
Welcome to our blog on the 10 danger signs of diabetes foot complications. If you or someone you know has diabetes, it is crucial to be aware of the potential foot problems that can arise. Diabetes can have a significant impact on your feet, increasing the risk of complications such as neuropathy, foot ulcers, and poor circulation. By understanding these danger signs, you can take proactive steps to prevent and manage foot complications, ultimately improving your overall health outcomes.
Understanding Diabetes and its Impact on Feet
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels. Over time, uncontrolled diabetes can damage blood vessels and nerves, leading to a variety of complications, including foot problems. Nerve damage, known as neuropathy, can cause numbness, tingling, and loss of sensation in the feet, making it difficult to detect injuries or ulcers. Poor blood flow, caused by damaged blood vessels, can impair wound healing, putting diabetic individuals at a higher risk of foot infections and amputation.
The Connection Between Diabetes and Foot Health
Diabetes and foot health are closely connected, and individuals with diabetes are more susceptible to foot complications. Peripheral artery disease (PAD), a condition characterized by narrowed blood vessels, is common among people with diabetes. PAD reduces blood flow to the feet, compromising their health and increasing the risk of foot ulcers and infections. It is essential for diabetic individuals to be aware of this connection and take proactive measures to maintain proper foot health.
How Diabetes Can Aggravate Common Foot Problems
In addition to nerve damage and poor blood flow, diabetes can aggravate common foot problems, making them more challenging to manage. High blood sugar levels can create an environment conducive to fungal infections, such as athlete’s foot, and other foot problems, including calluses, corns, and ingrown toenails. Diabetic neuropathy, a type of nerve damage associated with diabetes, can also lead to foot deformities, such as hammertoes and bunions. Proper foot care and blood sugar control are vital in preventing the worsening of these common foot problems.
Detailed Look at the 10 Danger Signs of Diabetes Foot Complications
Now, let’s take a closer look at the ten danger signs of diabetes foot complications. By being aware of these signs, you can detect problems early and seek prompt medical attention, reducing the risk of serious complications.
10 – Dry, Cracked Skin
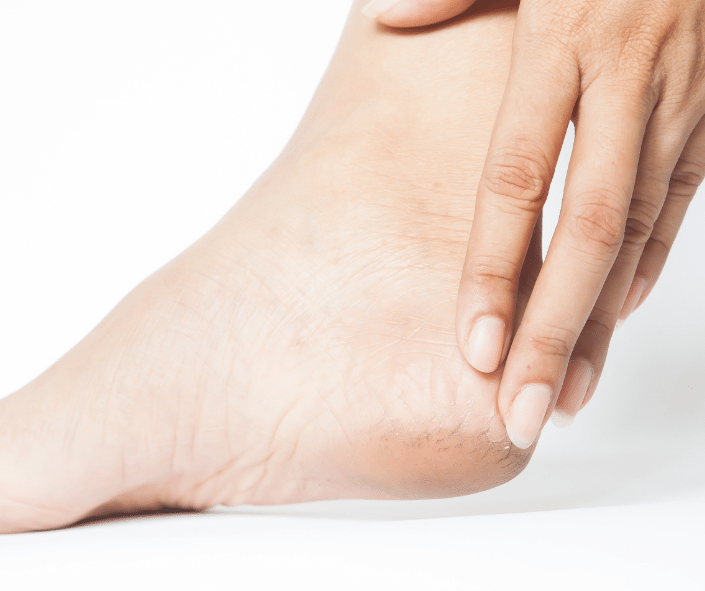
Dry, cracked skin is a common problem for people with diabetes, especially on the feet. Moisture loss is common due to nerve damage, which affects sweat glands, and poor blood flow to the feet. This can lead to cracks and sores, increasing the risk of infection. Regularly moisturizing diabetic feet, avoiding hot water, and wearing moisture-wicking socks can help prevent dry, cracked skin. Redness, swelling, or signs of infection in dry, cracked skin should be evaluated by a healthcare provider promptly to prevent serious complications.
9 – Ingrown Toenails
Ingrown toenails occur when the edges of the toenails grow into the surrounding skin, causing pain and inflammation. For individuals with diabetes, proper foot care is crucial in preventing complications related to ingrown toenails. It is essential to trim toenails straight across, avoid sharp edges, and wear shoes that provide adequate toe room. If you have an ingrown toenail, it is recommended to see a podiatrist, who can provide appropriate care, including toenail trimming or, in severe cases, surgical intervention.

8 – Calluses and Corn
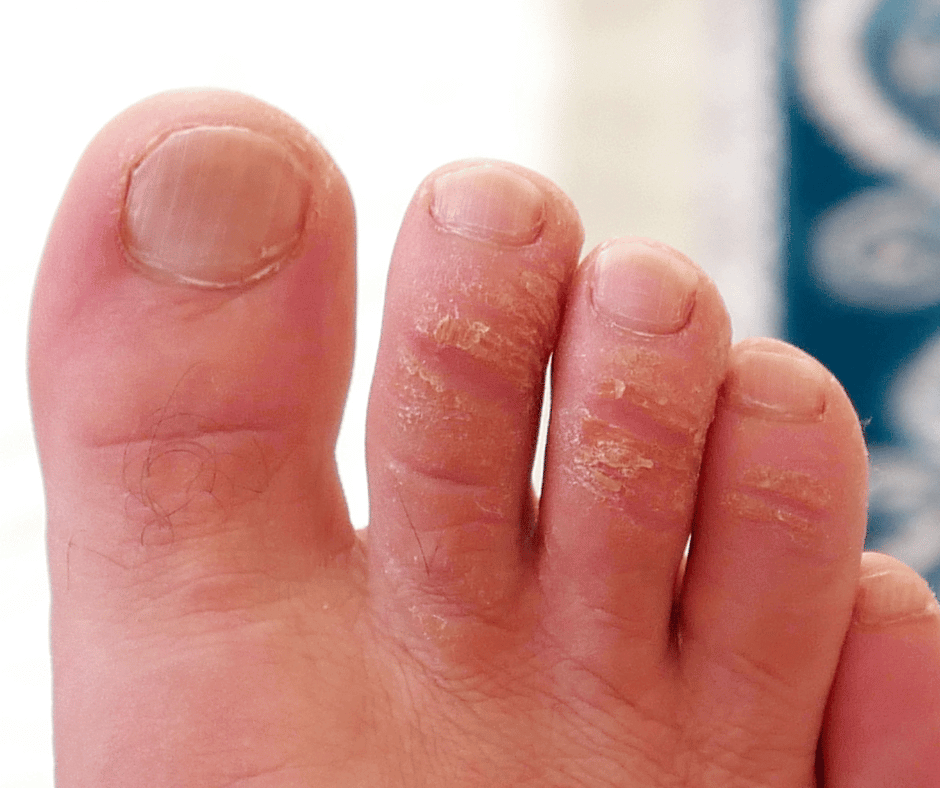
Diabetic feet require special attention to prevent complications associated with calluses and corns. Managing calluses and corns becomes more challenging due to diabetes, potentially leading to foot ulceration. Regular foot care is crucial for individuals with diabetes to avert serious foot problems. Neglecting calluses and corns in diabetic individuals can result in severe foot issues. Providing proper care for calluses and corns is essential to maintain foot health and overall well-being.
7 – Bunions
Bunions are bony protrusions that develop at the base of the big toe, often causing foot pain and deformities. Diabetes can exacerbate bunions, making them more challenging to manage. Individuals with diabetes should take special care with their choice of footwear to alleviate pressure on bunions. Custom shoes, orthotics, or cushioning pads can help provide relief. It is essential to seek podiatrist care for appropriate assessment and treatment of bunions, as severe cases may require surgical intervention.
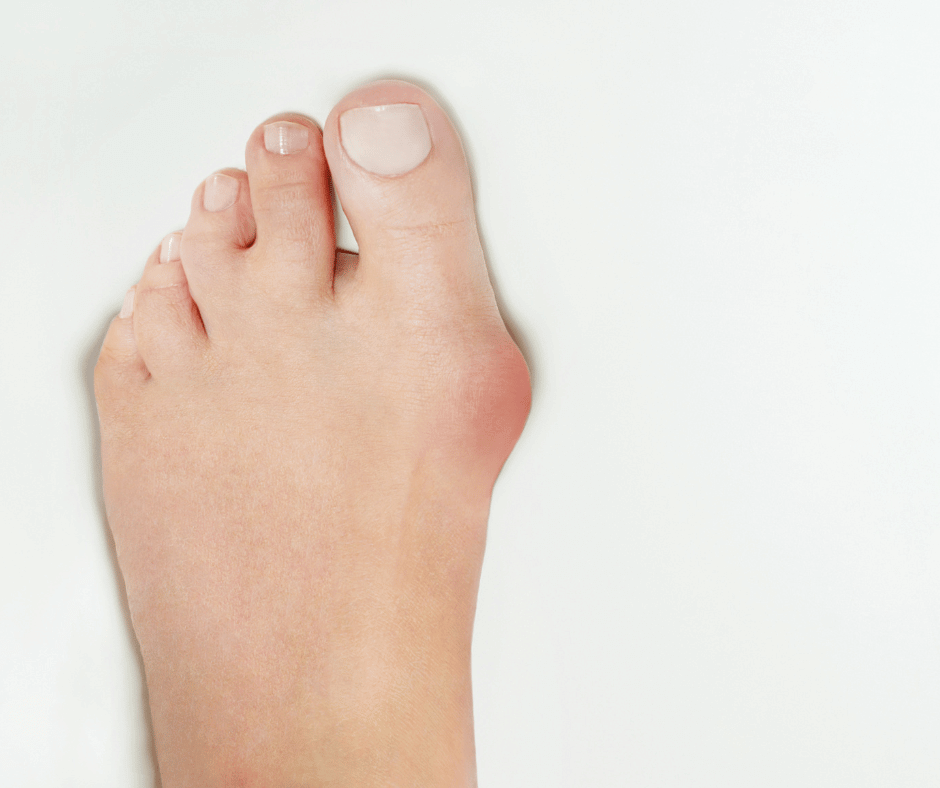
6 – Swelling and Redness
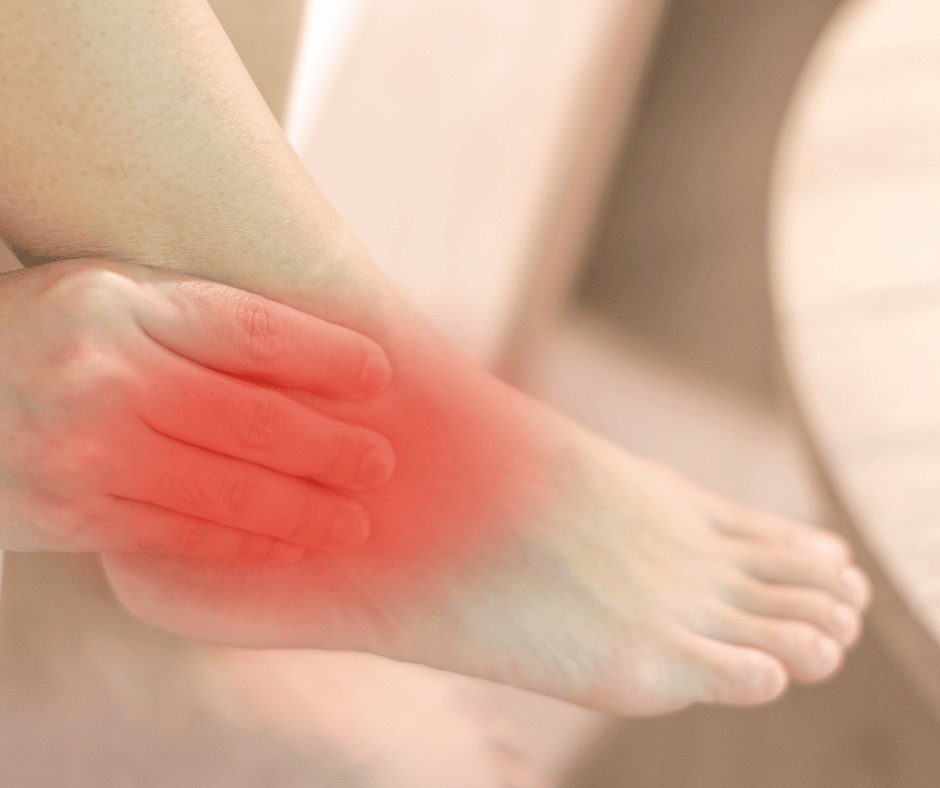
Swelling and redness in the feet can be warning signs of underlying foot complications in individuals with diabetes. Inflammation resulting from poor circulation or foot infection can cause localized redness and swelling. It is crucial to promptly address these symptoms to prevent serious complications. Elevating the feet, wearing comfortable shoes, and practicing good foot care can help manage swelling and redness. If these symptoms persist or worsen, it is important to seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
5 – Plantar Warts
Plantar warts, caused by a viral infection, can develop on the soles of the feet, causing discomfort or pain. Diabetic individuals should take special care in preventing and treating plantar warts, as they can lead to complications. Some key points to consider:
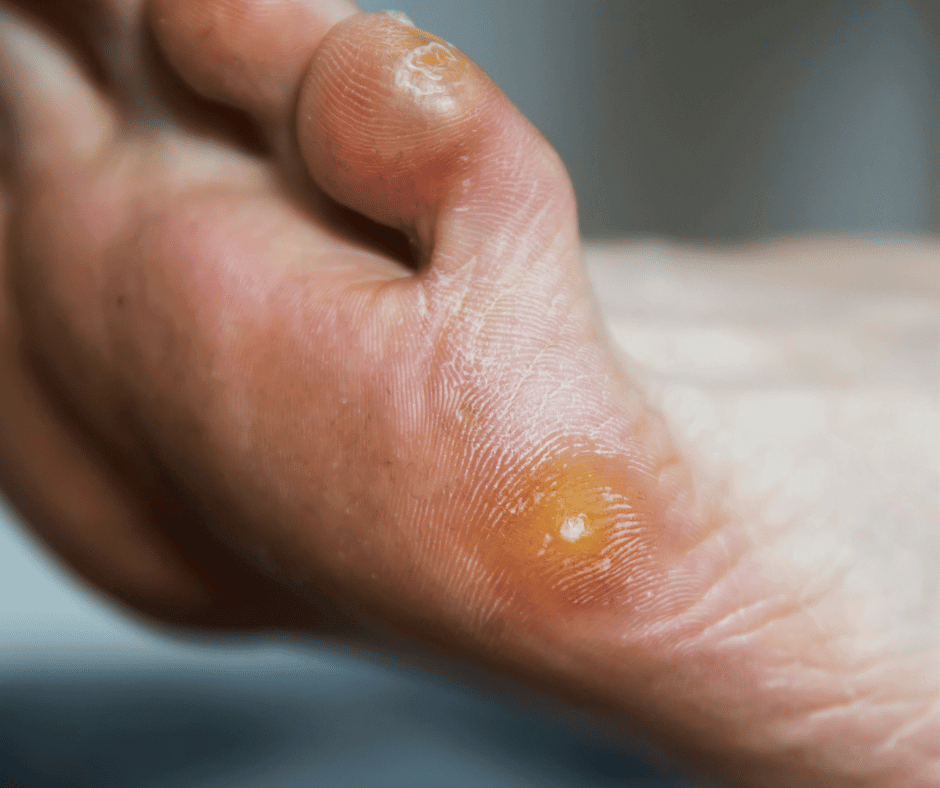
- Avoid walking barefoot in public areas to reduce the risk of contracting the virus.
- If you notice a plantar wart, avoid picking or scratching it, as it can spread the virus.
- Consult a foot doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment of plantar warts.
- Diabetic individuals should never attempt home remedies without consulting a healthcare professional.
- Regular foot exams can help detect plantar warts early, allowing for timely intervention.
4 – Neuropathy
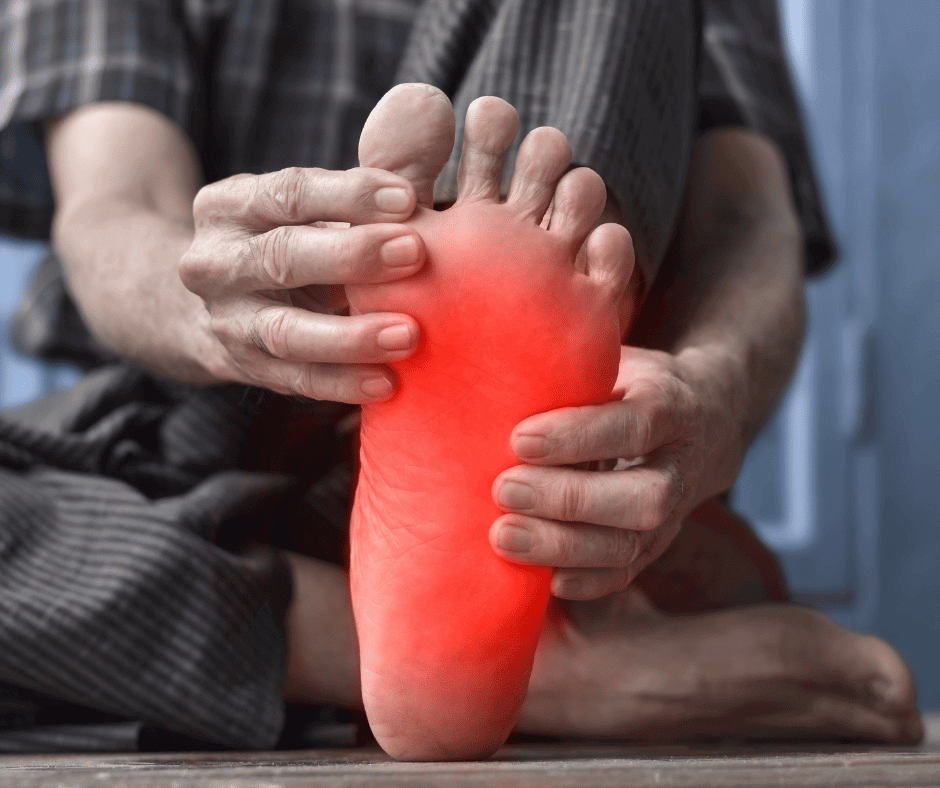
Neuropathy, a common complication of diabetes, affects the nerves in the feet, leading to symptoms such as numbness, tingling, and burning sensations. Diabetic neuropathy can significantly impact foot health, as it may cause a loss of sensation, making it difficult for diabetic individuals to detect injuries or ulcers. Proper foot care, regular foot exams, and maintaining good blood sugar control are pivotal in preventing and managing neuropathy. By addressing neuropathy early, diabetic individuals can reduce the risk of serious foot complications, such as ulcers and infections.
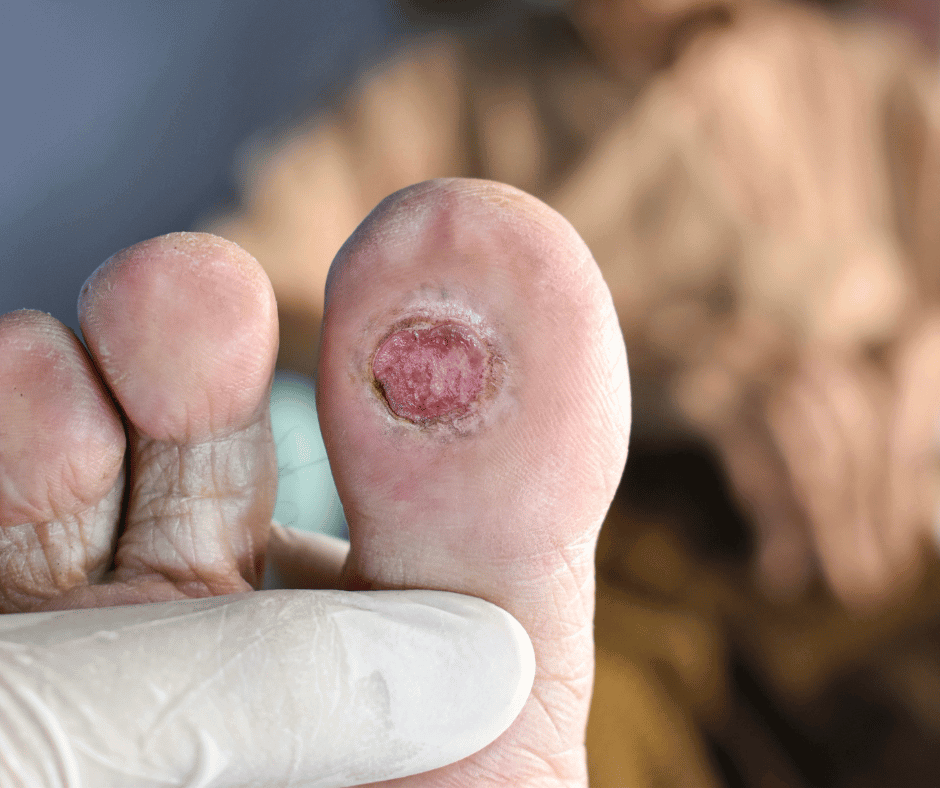
3- Ulcers
Ulcers, open sores common in people with diabetes, often stem from nerve damage or poor circulation. They pose a challenge to heal and heighten the risk of infection, gangrene, and amputation. Recognizable by redness, swelling, pain, and discharge, daily foot inspections are crucial for timely medical intervention. Prioritizing foot care and seeking prompt medical attention can significantly mitigate the risk of severe complications, including amputation.
2 – Charcot Foot
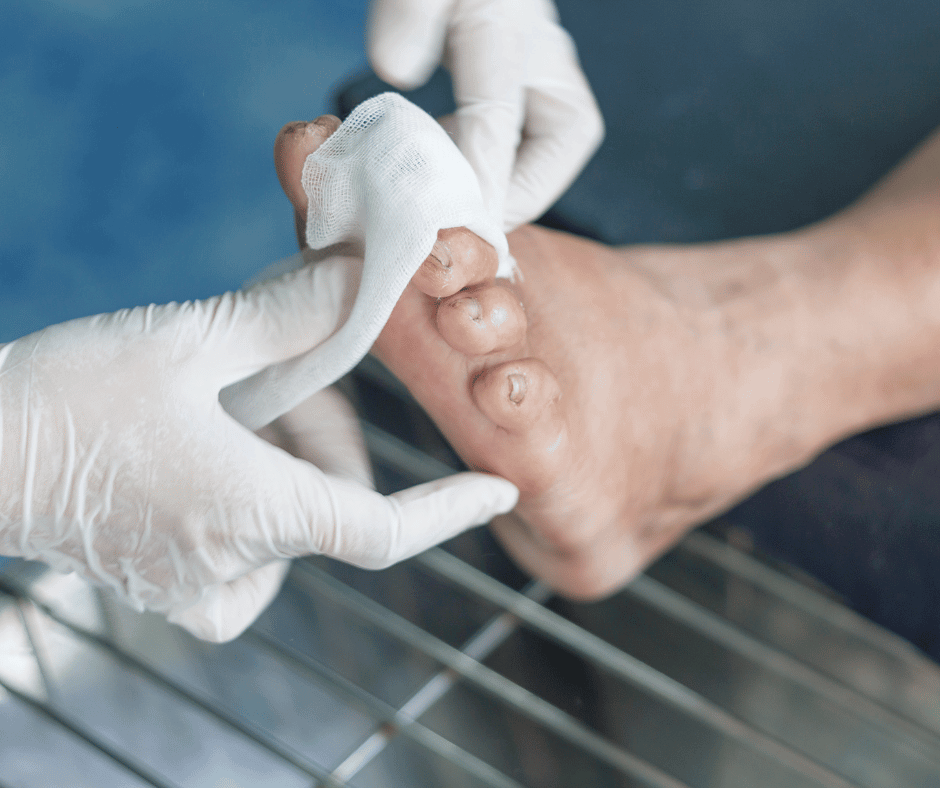

Charcot foot is a severe complication of diabetes characterized by weakened bones and foot deformities. Nerve damage, poor blood flow, and the shape of your feet can contribute to the development of Charcot foot. Diabetic individuals should be mindful of the warning signs, such as swelling, redness, and warmth in the affected foot. Prompt diagnosis and treatment, including immobilization, custom shoes or braces, and regular monitoring, are essential in managing Charcot foot and preventing further complications.
1 – Gangrene
Gangrene is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that can occur as a complication of diabetes foot problems. It is characterized by tissue death due to a lack of blood supply, often requiring amputation in severe cases. For individuals with diabetes, it is crucial to prioritize foot care and seek immediate medical attention for any signs of infection, slow-healing wounds, or severe pain. Proper glycemic control, regular foot examinations, and early intervention can help prevent gangrene and its associated complications, including amputation.
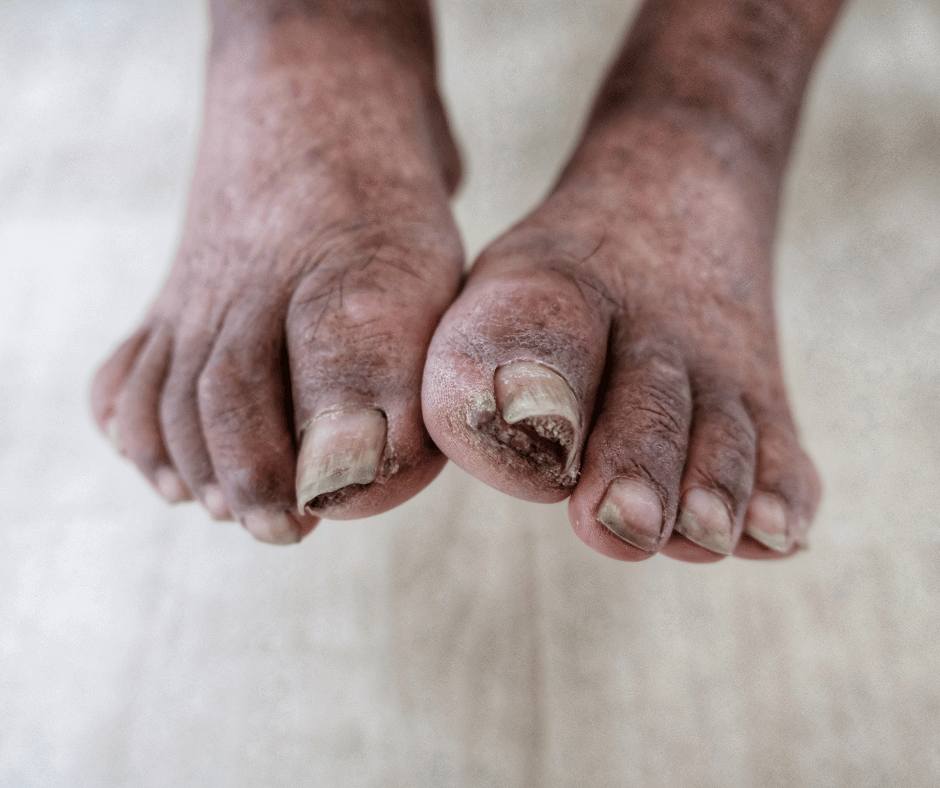
Preventive Measures for Diabetes Foot Complications
To prevent diabetes foot complications, proactive foot care and blood sugar control are essential. By incorporating simple yet effective preventive measures into your daily routine, you can significantly reduce the risk of serious foot problems. Proper foot care, regular foot check-ups, and adhering to your diabetes management plan can make a significant difference in maintaining foot health and preventing complications. Here are some tips to care for your feet if you have diabetes.
Tips to Care for Your Feet if You Have Diabetes
Taking good care of your feet is crucial if you have diabetes. Here are some tips to help you maintain foot health:
- Inspect your feet daily for any signs of redness, swelling, calluses, or sores.
- Wash your feet with mild soap and warm water, ensuring thorough drying, and apply lotion to prevent dry skin.
- Trim your toenails carefully, avoiding sharp edges, and seek professional help for foot care if needed.
- Wear properly fitting shoes that provide adequate support and cushioning, considering special diabetic shoes if recommended.
- Keep your feet protected from extreme temperatures, moisture, and pressure by wearing appropriate footwear.
- Consult with a foot protection team, including your healthcare provider, podiatrist, and diabetes care team, for tailored foot care guidance.
Importance of Regular Foot Check-ups
Regular foot check-ups are essential for diabetic individuals to detect and address potential foot complications early. Here’s why foot examinations are important:
- Thorough foot exams conducted by a healthcare provider, podiatrist, or foot protection team can identify any foot deformities, ulcerations, or circulation problems.
- Healthcare providers can assess blood pressure, blood flow, and nerve sensation to detect early signs of diabetic foot complications.
- Regular foot check-ups offer an opportunity to discuss concerns, address risk factors, and receive tailored guidance for foot care.
- Prompt identification of foot problems through regular examinations can prevent complications, such as foot ulcers, infections, and amputations, in diabetic individuals.
How to Respond to Diabetes Foot Complications
When faced with diabetes foot complications, it is crucial to respond promptly and seek appropriate medical care. Proper management of complications can help minimize their impact and prevent potentially serious consequences. If you notice any signs of foot complications, such as persistent pain, swelling, or non-healing wounds, it is essential to consult your healthcare provider. They can evaluate the situation, provide timely treatment, and coordinate with other specialists, such as podiatrists, vascular surgeons, or wound care experts, if needed.
When to See a Healthcare Provider
Knowing when to see a healthcare provider in the case of diabetic foot complications is crucial to prevent further damage or complications. Here are some situations where it is important to seek medical attention:
- Any signs of foot injury, infection, or persistent foot pain, especially for individuals with diabetes, warrant prompt evaluation by a healthcare provider.
- Diabetic individuals should consult their general practitioner (GP) or podiatrist if they notice any changes in foot shape, skin texture, or toenail abnormalities.
- If you experience numbness, tingling, or burning sensations in your feet, it is important to have a healthcare provider assess your nerve function.
- Promptly report foot problems, such as foot ulcers, calluses, or deformities, to your healthcare provider to prevent serious complications.
- Regular foot assessments by a podiatrist or healthcare provider are recommended for diabetic individuals to monitor foot health and potential risks of amputation.
Finding Support and Resources
Finding support and resources is crucial when managing diabetes foot complications. Here are some avenues to explore:
- Seek support from healthcare providers who specialize in diabetic foot care or diabetes management.
- Consider joining patient support groups or online communities to connect with others facing similar challenges.
- Explore resources provided by organizations, such as diabetes associations, that offer education on foot care, complications, and management strategies.
- Consult your healthcare provider about medicare options that may cover diabetic foot care or related services.
- Take advantage of diabetes education programs, workshops, or classes that provide valuable information on foot care and overall diabetes management.
How Does Proper Foot Care Benefit Overall Diabetes Management?
Proper foot care plays a crucial role in overall diabetes management. Here’s how it benefits individuals with diabetes:
- Good foot care helps prevent diabetic foot problems, such as ulcers, infections, and deformities, which can lead to serious complications.
- By maintaining good foot health, individuals can prevent complications that could negatively impact blood sugar levels, ultimately improving overall glucose control.
- Regular foot care and monitoring contribute to preventing severe foot complications, including gangrene, amputation, and related health issues.
- Prioritizing foot care supports a better quality of life, allowing individuals to stay active, mobile, and independent.
- Incorporating proper foot care into daily routines empowers individuals, ensuring they are proactive in managing their diabetes and preventing potential complications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is crucial to be aware of the danger signs of diabetes foot complications and take preventive measures to protect your foot health. Dry, cracked skin, ingrown toenails, calluses, bunions, swelling, redness, plantar warts, neuropathy, ulcers, Charcot foot, and gangrene are all potential complications that should not be ignored. Regular foot check-ups and proper foot care are essential for managing diabetes and preventing further complications. If you notice any warning signs or symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention promptly. By staying proactive and informed, you can overcome the challenges associated with diabetes foot complications and ensure better overall diabetes management. Remember, taking care of your feet is an integral part of maintaining your overall health and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some of the most common foot complications associated with diabetes?
Common foot complications associated with diabetes include neuropathy, foot ulcers, and peripheral vascular disease. These complications can significantly impact foot health and overall well-being. Neuropathy, damage to the nerves, often leads to numbness, tingling, or burning in the feet, making it difficult to detect injuries or wounds. Foot ulcers, open sores, can develop due to poor circulation or nerve damage, necessitating immediate medical attention to prevent infection or amputation. Peripheral vascular disease, affecting blood vessels, reduces blood flow to the feet, increasing the risk of complications. Individuals with diabetes should prioritize foot care and seek professional advice to prevent, manage, and address these common foot complications effectively.
How can I prevent or manage foot complications if I have diabetes?
Preventing and managing foot complications in diabetes requires a comprehensive approach. Here are some tips to help you:
- Practice good foot care, including daily inspection, washing with mild soap and warm water, and thorough drying.
- Control your blood sugar levels through proper diet, medication, and regular monitoring.
- Engage in physical activity to improve circulation and overall foot health, considering low-impact exercises such as walking or swimming.
- Wear properly fitting shoes and socks to reduce pressure, friction, and the risk of injury.
- Avoid smoking, as it can impair circulation and slow healing of foot wounds.
- Work closely with your healthcare provider to develop an individualized foot care plan and address any potential complications promptly.
What are some warning signs that indicate I may be developing foot complications related to diabetes?
Several warning signs may indicate the development of foot complications associated with diabetes. It is crucial to be vigilant and seek medical attention if you notice the following:
- Numbness or tingling sensations in the feet, which may indicate nerve damage.
- Persistent foot pain or discomfort, especially during walking, which can signify underlying problems.
- Skin changes, such as redness, swelling, calluses, or corns, that may indicate pressure points, foot deformities, or poor blood flow.
- Skin infections, sores, or slow-healing wounds, which can be potential signs of diabetic foot ulcers.
- Any noticeable changes in foot shape, toenails, or overall foot health, including deformities, discoloration, or increased foot temperature.
How can diabetes impact circulation and nerve function in my feet?
Diabetes can have a significant impact on circulation and nerve function in the feet. Here’s how it happens:
- High blood sugar levels associated with diabetes can damage small blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the feet.
- Nerve damage, known as peripheral neuropathy, is a common complication of diabetes, leading to numbness, tingling, and loss of sensation in the feet.
- Poor blood flow and nerve damage can impair the foot’s ability to heal, increasing the risk of complications, such as infections, ulcers, or even amputation.
- Diabetic foot complications can arise due to a combination of poor circulation, neuropathy, and impaired wound healing, highlighting the importance of regular foot care and monitoring.