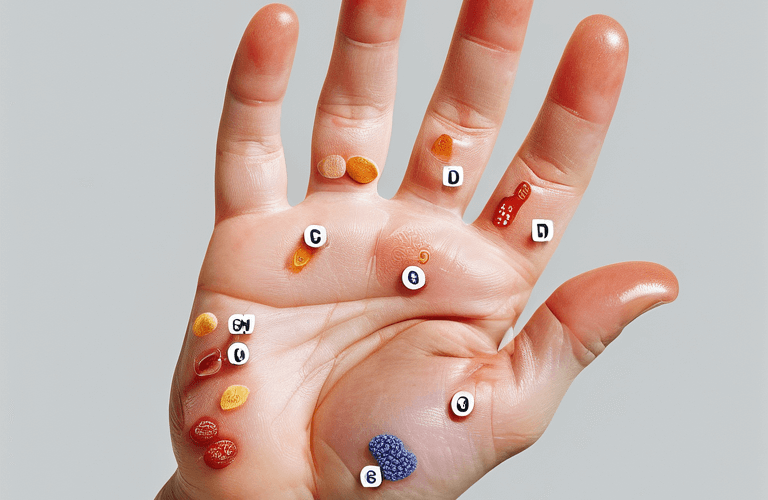
Introduction
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While most people are aware of the common symptoms and complications of diabetes, many may not realize that diabetes can also have an impact on the skin. Skin problems, such as dark patches, skin tags, and fungal infections, can be surprising signs of diabetes, according to the American Diabetes Association (ADA). These skin signs may occur due to factors such as insulin resistance, nerve damage, and high blood sugar levels.
In this blog, we will explore seven surprising signs of diabetes on the skin and understand the causes behind these skin changes. We will also discuss preventive measures, treatment options, and the connection between diet, exercise, and skin health. Additionally, we will address common questions about diabetes-related skin signs.
Understanding and recognizing these skin signs is crucial for early detection and prevention of complications. By taking proactive measures to manage blood sugar levels and maintain overall health, individuals with diabetes can minimize the impact of these skin problems and improve their quality of life. So let’s dive in and uncover the surprising diabetes skin signs.
7 Surprising Signs of Diabetes on Your Skin
1. Dark Skin Patches (Acanthosis Nigricans)
Dark skin patches, known as acanthosis nigricans, are a common skin sign of diabetes. These patches appear as dark, velvety areas of skin, usually in body folds such as the back of the neck, armpits, groin, elbows, and knees. Acanthosis nigricans is often associated with insulin resistance, a condition in which the body’s cells become less responsive to the effects of insulin. Insulin resistance can lead to higher levels of insulin in the blood, which can stimulate the growth of skin cells and cause the characteristic dark patches.
The exact cause of acanthosis nigricans is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to the overstimulation of skin cells by insulin. The condition may also be associated with other underlying health issues, such as obesity, hormonal disorders, certain medications, and certain types of cancer. In some cases, acanthosis nigricans may resolve with weight loss and improved blood sugar control. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and management of this skin condition.
2. Skin Tags (Acrochordons)
Skin tags, medically known as acrochordons, can be a surprising sign of diabetes. These small, flesh-colored growths commonly appear in areas where skin rubs together, like the neck, armpits, or groin. While not exclusive to diabetes, their presence may indicate high blood sugar levels or insulin resistance. Individuals with uncontrolled diabetes or metabolic syndrome are at higher risk of developing skin tags. Managing blood glucose levels through lifestyle changes or medical interventions can sometimes help reduce the occurrence of these skin growths. Consulting with a healthcare provider for a comprehensive treatment plan is advisable to address both the skin tags and the underlying diabetes condition effectively.
3. Tingling Feet (Neuropathy)
Diabetic neuropathy, a common complication of diabetes, can cause tingling, numbness, or a burning sensation in the feet. This condition occurs when high blood glucose levels damage the nerves, impairing their ability to transmit signals properly. Tingling feet can be a surprising sign of diabetes and should not be ignored.
Prolonged exposure to high blood glucose levels can lead to nerve damage and diabetic neuropathy. The exact mechanism behind this damage is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to a combination of factors, including metabolic changes, inflammation, and oxidative stress.
The tingling sensation in the feet is often described as a “pins and needles” feeling or a sensation similar to small electric shocks. It can be intermittent or constant and may worsen at night. If left unmanaged, diabetic neuropathy can progress and cause more severe symptoms, such as muscle weakness, loss of balance, and foot ulcers. Understanding the pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy is crucial in preventing and managing this common complication of diabetes.
Proper blood glucose management is essential for preventing and managing diabetic neuropathy. Maintaining target blood glucose levels through diet, exercise, and medication can help slow the progression of nerve damage and alleviate symptoms. Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels and routine foot care are also important for early detection and prevention of complications associated with diabetic neuropathy.
4. Fungal Toenail (Onychomycosis)
Onychomycosis, commonly known as a fungal toenail infection, is a common skin sign of diabetes. This condition occurs when fungi, such as dermatophytes, invade the nails, causing them to become discolored, thickened, and brittle. People with diabetes are more susceptible to onychomycosis due to factors such as compromised immune function and poor blood circulation, as well as the potential development of diabetic ketoacidosis.
Fungal toenail infections often start as athlete’s foot, a common fungal infection that affects the skin between the toes. If left untreated, the infection can spread to the nails, leading to onychomycosis or athlete’s foot on the feet. The warm and moist environment inside shoes provides an ideal breeding ground for fungi, making the feet vulnerable to infections.
Proper foot hygiene and regular inspection of the feet can help prevent fungal toenail infections. It is important to keep the feet clean and dry, wear breathable footwear, and change socks regularly. If a fungal infection is suspected, it is important to seek treatment to prevent the infection from spreading and causing further complications. Treatment options for onychomycosis include topical antifungal medications, oral antifungal medications, and in severe cases, surgical removal of the infected nail.
5. Shin Spots (Diabetic Dermopathy)
Diabetic dermopathy, also known as shin spots, is a skin condition characterized by reddish-brown patches on the shins. These patches may appear flat and slightly scaly, and they are often more noticeable in individuals with fair skin. Diabetic dermopathy is a common skin sign of diabetes and can be a result of small blood vessels leaking under the skin. It has a strong predilection for men and those older than 50 years of age, making it an important skin sign to look out for in this demographic.
The exact cause of diabetic dermopathy is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to microvascular complications associated with diabetes. High blood glucose levels can damage the small blood vessels that supply nutrition and oxygen to the skin, leading to the development of shin spots.
While diabetic dermopathy is generally harmless and does not require treatment, it can serve as a warning sign of more serious complications related to diabetes, such as retinopathy, neuropathy, or kidney disease. If you notice any skin changes or have concerns about your skin health, it is important to consult with a dermatologist or healthcare professional for proper evaluation and management.
6. Hard Skin On Fingers (Digital Sclerosis)
Digital sclerosis is a skin condition that causes the skin on the fingers, and sometimes toes, to become thick, tight, waxy, and potentially stiff. This condition is more common in individuals with type 1 diabetes and is believed to be associated with high blood sugar levels.
The exact mechanism behind the development of digital sclerosis is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to the accumulation of glycosaminoglycans, a type of sugar molecule, in the skin and soft tissues. High blood sugar levels can contribute to the formation of these molecules, leading to the characteristic hardening and thickening of the skin.
Digital sclerosis can affect the finger joints, making them harder to move and potentially causing discomfort and limited mobility. Proper blood sugar control is the only treatment for digital sclerosis. Additionally, moisturizers and lotions can help soften the skin and improve flexibility. If you notice any changes in your skin or joint function, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and management.
7. Skin Bumps (Eruptive Xanthomatosis)
Eruptive Xanthomatosis is a dermatological condition characterized by small yellow skin bumps, often encircled by red halos. This condition is commonly observed in individuals with uncontrolled diabetes and elevated blood cholesterol levels, stemming from the accumulation of excessive lipids in the skin. The itchy and sometimes painful bumps typically appear on areas such as the buttocks, shoulders, and the extensor surfaces of the arms and legs, and are more likely to occur in young men with high cholesterol and triglycerides.
For individuals with diabetes who develop eruptive xanthomatosis, it is imperative to effectively manage their blood sugar and cholesterol levels. These skin manifestations can serve as indicators of underlying metabolic issues that need to be addressed promptly. Seeking professional medical advice from a healthcare provider is essential for an accurate diagnosis and the development of personalized treatment plans tailored to each individual’s needs.
In addition to managing blood sugar and cholesterol levels, lifestyle modifications such as adopting a healthy diet low in saturated fats and sugars can also play a crucial role in managing eruptive xanthomatosis. Regular monitoring and follow-ups with healthcare providers are essential to track progress and ensure optimal management of this skin condition.
Understanding the Causes Behind Diabetes Skin Signs
Understanding the underlying causes of diabetes-related skin signs is essential for proper management and prevention of complications. The main factors contributing to these skin signs include blood sugar control, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome.
Blood sugar control plays a crucial role in managing diabetes-related skin problems. Prolonged exposure to high blood glucose levels can lead to damage in blood vessels and nerves, compromising the skin’s health. Proper management of blood sugar levels through lifestyle modifications, medication, and regular monitoring is crucial for preventing and managing skin complications caused by high blood sugar over a long time.
Insulin resistance is another key factor in the development of diabetes-related skin signs. Insulin resistance occurs when the body’s cells become less responsive to the effects of insulin, resulting in elevated blood sugar levels. This can lead to the growth of skin cells, hyperpigmentation, and other skin changes commonly seen in individuals with diabetes.
Metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions including high blood pressure, high blood sugar, excess body fat, and abnormal cholesterol levels, is closely associated with diabetes-related skin signs. Metabolic syndrome can contribute to insulin resistance and other metabolic abnormalities, increasing the risk of skin complications.
By understanding the underlying causes of diabetes-related skin signs, individuals with diabetes can take proactive measures to manage their blood sugar levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and minimize the risk of skin complications.
The Role of Blood Sugar Control
Proper blood sugar control is essential for preventing and managing diabetes-related skin signs. High blood sugar levels can lead to damage in blood vessels, nerves, and skin cells, increasing the risk of skin complications. Conversely, maintaining target blood glucose levels can help minimize the impact of diabetes on the skin.
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is crucial for understanding the effect of diet, exercise, and medication on blood glucose levels. This information can guide individuals with diabetes in making necessary adjustments to their treatment plan and lifestyle habits to achieve optimal blood sugar control.
In addition to monitoring blood sugar levels, adopting a healthy diet and engaging in regular physical activity can support blood sugar control and overall skin health. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help regulate blood glucose levels and provide essential nutrients for skin health.
Proper blood sugar control is a cornerstone of diabetes management and plays a significant role in preventing and managing diabetes-related skin signs. Working closely with healthcare professionals and following a personalized treatment plan can help individuals with diabetes achieve and maintain target blood glucose levels.
Insulin Resistance and Skin Changes
Insulin resistance, a hallmark of type 2 diabetes, can have a significant impact on the skin. Insulin resistance occurs when the body’s cells become less responsive to the effects of insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. This can contribute to the development of various skin changes, including acanthosis nigricans.
Acanthosis nigricans is characterized by dark, velvety patches of skin, usually in body folds such as the neck, armpits, groin, elbows, and knees. These skin changes are believed to be a result of the overstimulation of skin cells by insulin. Insulin resistance can lead to higher levels of insulin in the blood, stimulating the growth of skin cells and causing the characteristic dark patches.
Proper management of insulin resistance, through lifestyle modifications, medication, and regular monitoring, is crucial for minimizing the impact of insulin resistance on the skin. By achieving and maintaining target blood glucose levels, individuals with insulin resistance can reduce the risk of skin complications and improve overall skin health.
Preventive Measures and Early Detection
Preventive measures and early detection are vital for managing diabetes-related skin signs and preventing complications. The following steps can help individuals with diabetes maintain healthy skin:
- Regular Monitoring for Skin Changes: Regularly inspecting the skin for any changes, such as dark patches, skin tags, or dry skin, can help identify potential skin complications early. If any abnormalities are noticed, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and management.
- Importance of Blood Glucose Management: Proper blood glucose management is crucial for preventing and managing diabetes-related skin signs. Maintaining target blood glucose levels through diet, exercise, medication, and regular monitoring can help minimize the impact of diabetes on the skin.
- Maintaining a Healthy Immune System: The immune system plays a vital role in protecting the skin from infections and promoting wound healing. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management, can support immune function and overall skin health.
By practicing preventive measures and early detection, individuals with diabetes can take proactive steps to protect their skin and minimize the risk of complications. Regular communication with healthcare professionals is essential for proper evaluation, monitoring, and management of diabetes-related skin signs.
Regular Monitoring for Skin Changes
Regular monitoring of the skin is crucial for individuals with diabetes to detect any changes or abnormalities early. By inspecting the skin regularly, individuals can identify potential skin complications and take appropriate measures to prevent further progression or complications.
Key areas to pay attention to during skin monitoring include body folds, such as the neck, armpits, groin, elbows, and knees. These areas are more prone to developing skin changes, such as acanthosis nigricans or skin tags. Additionally, individuals should check their feet daily, as foot complications are common in diabetes.
If any changes or abnormalities are noticed, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional or dermatologist for proper evaluation and management. Early detection and intervention can help prevent the progression of skin complications and minimize the impact on overall health and well-being.
Importance of Blood Glucose Management
Proper blood glucose management is essential for maintaining healthy skin and preventing diabetes-related skin complications. High blood glucose levels can contribute to the development of skin problems and increase the risk of infections, delayed wound healing, and other skin complications.
To effectively manage blood glucose levels, individuals with diabetes should adhere to their treatment plan, which may include medication, diet modifications, regular exercise, and routine blood glucose monitoring. Regular communication with healthcare professionals is essential for determining target blood glucose levels and making necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
By maintaining target blood glucose levels, individuals can minimize the impact of diabetes on the skin and reduce the risk of complications. Proper blood glucose management is a cornerstone of diabetes care and should be prioritized for overall health and well-being.
Treatment Options for Diabetes-Related Skin Problems
Various treatment options are available for managing diabetes-related skin problems. The choice of treatment depends on the specific skin problem and its severity. Here are some common treatment options:
- Topical Treatments and Creams: Topical treatments such as creams, ointments, and lotions can be used to alleviate symptoms associated with skin conditions like dryness, itchiness, and inflammation. These treatments may include moisturizers, corticosteroids, antifungal creams, or antibacterial ointments.
- When to See a Dermatologist: In some cases, it may be necessary to seek the expertise of a dermatologist for proper evaluation and management of skin problems. Dermatologists can provide specialized treatments, such as laser therapy, cryotherapy, or prescription medications, to address specific skin conditions.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for managing diabetes-related skin problems. Regular follow-up appointments and open communication with healthcare professionals are essential for monitoring the progress of treatment and making necessary adjustments.
Topical Treatments and Creams
Topical treatments and creams can be effective for managing various skin disorders associated with diabetes. These treatments are applied directly to the affected areas of the skin and can help alleviate symptoms such as dryness, itchiness, inflammation, or infections.
For dry skin, moisturizers and emollients can provide hydration and improve the skin’s barrier function. These products should be applied regularly, especially after bathing, to lock in moisture and prevent dryness.
For skin infections, topical antifungal or antibacterial creams may be prescribed to target the underlying cause of the infection. These creams can help eliminate the microorganisms responsible for the infection and promote healing.
Corticosteroid creams or ointments may be recommended for managing inflammation and itchiness associated with certain skin conditions. These medications can help reduce inflammation and provide relief from symptoms.
It is important to follow the instructions provided by healthcare professionals and use topical treatments and creams as directed. If symptoms persist or worsen, it may be necessary to consult with a healthcare professional for further evaluation and management.
When to See a Dermatologist
While some diabetes-related skin problems can be managed with over-the-counter treatments, it may be necessary to consult with a dermatologist for proper evaluation and management. Dermatologists are specialized healthcare professionals who can provide expertise in diagnosing and treating a wide range of skin conditions.
It is recommended to see a dermatologist for the following reasons:
- Diagnosis of Skin Problems: Dermatologists can accurately diagnose the specific skin problem and determine the underlying cause. This is important for developing an appropriate treatment plan.
- Specialized Treatment Options: Dermatologists can provide specialized treatments, such as laser therapy, cryotherapy, or prescription medications, to address specific skin conditions. These treatments may be more effective in managing certain skin problems.
- Guidance on Treatment Options: Dermatologists can provide guidance on the most appropriate treatment options for managing diabetes-related skin problems. They can tailor the treatment plan to the individual’s specific needs and preferences.
If you are experiencing persistent or severe skin problems associated with diabetes, it is recommended to consult with a dermatologist for expert evaluation and management.
The Connection Between Diet, Exercise, and Skin Health
The connection between diet, exercise, and skin health is significant, especially in individuals with diabetes. A healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet and regular physical activity can have a positive impact on overall health, including the health of the skin.
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats provides essential nutrients that support skin health. These nutrients can help maintain the skin’s integrity, promote collagen production, and protect against oxidative damage.
Regular exercise improves blood circulation, which is important for delivering oxygen and nutrients to the skin. Exercise also helps reduce stress levels, which can have a positive impact on skin health.
By adopting a healthy diet and exercise routine, individuals with diabetes can support their skin health and minimize the risk of skin complications. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or nutritionist for personalized dietary recommendations and exercise guidelines.
Foods to Favor for Skin Health
A healthy diet plays a crucial role in promoting skin health, especially in individuals with diabetes. Certain foods are particularly beneficial for supporting skin health and maintaining blood sugar control. Here are some foods to favor for skin health:
- Fruits and Vegetables: Fruits and vegetables are rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that support skin health. Berries, leafy greens, tomatoes, and citrus fruits are particularly beneficial due to their high antioxidant content.
- Whole Grains: Whole grains, such as quinoa, brown rice, and whole wheat, provide fiber and essential nutrients that support stable blood sugar levels and overall skin health.
- Lean Proteins: Lean proteins, such as poultry, fish, tofu, and legumes, provide essential amino acids for collagen production and skin repair.
- Healthy Fats: Healthy fats, found in foods like avocados, nuts, and olive oil, provide omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants that support skin health and reduce inflammation.
By incorporating these foods into a balanced diet, individuals with diabetes can promote skin health and maintain stable blood sugar levels. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or nutritionist for personalized dietary recommendations based on individual needs and preferences.
Beneficial Exercises for Skin and Blood Sugar
Regular exercise is not only beneficial for overall health but also has a positive impact on skin health and blood sugar control in individuals with diabetes. Here are some exercises that can promote skin health and help maintain stable blood sugar levels:
- Aerobic Exercise: Activities such as walking, jogging, cycling, swimming, and dancing can improve blood circulation and promote overall cardiovascular health. Improved blood circulation helps deliver oxygen and essential nutrients to the skin, supporting its health and vitality.
- Strength Training: Strength training exercises, such as weightlifting and resistance training, can help build muscle mass and improve insulin sensitivity. Increased insulin sensitivity can contribute to better blood sugar control and reduce the risk of skin complications associated with diabetes.
- Yoga and Pilates: Yoga and Pilates promote flexibility, balance, and relaxation. These exercises can help reduce stress levels, which can have a positive impact on skin health and blood sugar control.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or certified fitness instructor before starting an exercise routine, especially if you have diabetes. They can provide guidance on the most appropriate exercises based on individual needs and health conditions.
Complications: When to Be Concerned
While many diabetes-related skin signs are generally harmless, certain complications may arise that require prompt medical attention. Here are some complications associated with diabetes-related skin problems:
- Signs of Infections: Skin infections, such as bacterial or fungal infections, can occur in individuals with diabetes. Signs of infection include redness, swelling, warmth, tenderness, and pus or discharge. Prompt medical attention and appropriate treatment are necessary to prevent the spread of the infection.
- Symptoms Indicating Poor Circulation: Poor circulation is common in individuals with diabetes and can affect the lower legs and feet. Symptoms of poor circulation include cold feet, numbness or tingling, slow-healing wounds, and changes in skin color. Proper management of blood sugar levels and regular foot care are essential for preventing complications associated with poor circulation.
If you experience any of these complications or have concerns about your skin health, it is important to seek prompt medical attention. Proper evaluation and management can help prevent further complications and ensure optimal skin health.
Signs of Infections
Skin infections are common in people with diabetes and can be caused by bacteria or yeast. Bacterial infections, such as styes, boils, folliculitis, and infections around the nails, can occur more frequently in individuals with diabetes. Symptoms of bacterial skin infections include pain, warmth, swelling, and redness, particularly around the hair follicles. These infections can be treated with antibiotic creams or pills.
Yeast infections, particularly those caused by Candida albicans, are also more common in people with diabetes. Symptoms of yeast infections include red, itchy, swollen skin with blistering or dry scales. Common areas affected by yeast infections include warm folds of the skin, such as under the breasts, in the groin, in the armpits, in the corners of the mouth, and under the foreskin of the penis. Other fungal infections, such as ringworm, jock itch, athlete’s foot, and vaginal yeast infections, are also common in diabetics. Antifungal medications are typically used to treat these infections.
Proper hygiene, such as keeping the skin clean and dry, can help prevent these infections. It’s important to seek medical treatment if you suspect a skin infection, as prompt treatment can prevent complications.
Symptoms Indicating Poor Circulation
Poor circulation is a common problem in people with diabetes and can lead to skin issues. When blood vessels and nerves are damaged, circulation is reduced, particularly in the lower legs. This can cause changes in the texture, appearance, and color of the skin.
Symptoms of poor circulation include itchy skin, particularly in the lower legs, as well as dryness and a decreased ability to sweat. Poor circulation can also make the skin more sensitive to temperature and pressure, leading to discomfort or pain.
It’s important to take measures to improve circulation, such as regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding smoking. Proper blood sugar management is also crucial for preventing and managing circulation problems. If you notice any symptoms of poor circulation, it’s important to consult with your healthcare provider for appropriate evaluation and treatment.
Real-Life Stories: Managing Skin Signs of Diabetes
Real-life stories of individuals managing skin signs of diabetes can provide valuable insights and inspiration. These stories highlight the importance of proper diabetes management, including blood sugar control and good hygiene practices.
By taking proactive steps, such as monitoring blood sugar levels, following a healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, and following their healthcare provider’s recommendations, these individuals have been able to effectively manage their skin conditions.
These success stories demonstrate the positive impact that lifestyle changes, medication adherence, and regular check-ups can have on overall skin health and diabetes management. By learning from these experiences, individuals with diabetes can gain valuable knowledge and motivation to take control of their own skin health.
Success Stories in Managing Skin Conditions
One success story involves a woman who was diagnosed with type 2 diabetes and developed skin conditions such as ulcers and slow wound healing. By making lifestyle changes, including adopting a healthier diet and increasing physical activity, she was able to successfully manage her blood sugar levels and improve her overall health.
Another success story features a man who struggled with diabetic dermopathy, a skin condition characterized by light brown patches on the shins. Through regular monitoring of his blood sugar levels and proper medication management, he was able to effectively control his diabetes and reduce the appearance of the skin patches.
These success stories highlight the importance of lifestyle changes, medication adherence, and regular monitoring in managing skin conditions associated with diabetes. By following these examples, individuals with diabetes can improve their skin health and overall well-being.
Tips from Patients and Doctors
Patients and doctors offer valuable tips for managing diabetes-related skin conditions:
- Regularly check your skin for any changes, such as ulcers, rashes, or dryness. Early detection can help prevent complications.
- Practice good hygiene, including keeping the skin clean and dry, particularly in areas prone to sweat or moisture.
- Moisturize your skin regularly to prevent dryness and cracking.
- Wear comfortable shoes and socks that fit well to prevent foot injuries and infections.
- Follow a healthy diet and exercise regularly to maintain overall health and well-being.
- Take prescribed medications as directed and keep regular appointments with your healthcare provider for diabetes management.
- Seek medical advice if you notice any concerning skin changes or if you have difficulty managing your blood sugar levels.
By following these tips, individuals with diabetes can take proactive steps to prevent and manage skin conditions associated with their condition.
Conclusion
In conclusion, recognizing the skin signs of diabetes is crucial for early detection and management. From dark patches to tingling feet, understanding these indicators can lead to timely preventive measures and treatment. Maintaining blood sugar levels, seeking dermatological advice when needed, and adopting a healthy lifestyle are key steps in managing diabetes-related skin issues. By prioritizing skin health alongside diabetes care, individuals can enhance their overall well-being and quality of life. Stay informed, stay vigilant, and prioritize your skin health to navigate the complexities of diabetes with confidence and knowledge.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can diabetes skin signs be reversed?
While some skin signs of diabetes can be managed and improved with proper treatment and lifestyle changes, it may not be possible to completely reverse these signs. However, with diligent management of blood sugar levels, good hygiene practices, and regular medical care, individuals can effectively manage their skin conditions and prevent further complications.
How do I differentiate between common skin issues and diabetes-related skin signs?
Differentiating between common skin issues and diabetes-related skin signs can be challenging. It’s important to consult with a dermatologist for a proper diagnosis. The dermatologist can evaluate the skin condition, consider the individual’s medical history and symptoms, and provide appropriate treatment recommendations.
Are these skin signs exclusive to Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes?
These skin signs can occur in both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. However, the severity and frequency of skin conditions may vary between the two types. It’s important for individuals with either type of diabetes to be aware of these potential skin signs and work with healthcare providers to manage their condition effectively.
What skincare products are recommended for someone with diabetes?
For individuals with diabetes, it is recommended to use gentle skincare products and mild soap. Avoid harsh cleansers and opt for moisturizers that are fragrance-free and hypoallergenic. It’s important to keep the skin clean, moisturized, and protected from excessive dryness or damage.
How often should someone with diabetes check their skin for changes?
Individuals with diabetes should regularly check their skin for any changes, such as ulcers, rashes, or dryness. The frequency of skin checks may vary depending on individual circumstances, but it is generally recommended to check the skin at least once a day. Early detection of skin changes can help prevent complications and ensure prompt treatment.